Teleostei >
Clupeiformes (Herrings) >
Alosidae (Shads and Sardines)
Etymology: Alosa: Latin, alausa = a fish cited by Ausonius and Latin, halec = pickle, dealing with the Greek word hals = salt; it is also the old Saxon name for shad = "alli" ; 1591 (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Lacepède.
Issue
5 subspecies known.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / 深度上下限 / distribution range
生態學
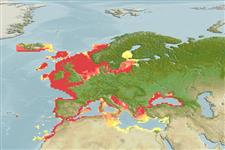
海洋; 淡水; 半鹹淡水 pelagic-neritic; 溯河洄游 (Ref. 51243); 深度上下限 10 - 400 m (Ref. 2945). 溫帶; 66°N - 27°N, 25°W - 42°E
Northeast Atlantic: Atlantic coasts from southern and western Iceland to northern Morocco (Ref. 188, 6683), including North Sea (Ref. 6683), Baltic Sea (Ref. 188, 6683); also Mediterranean Sea (Ref. 188, 3397, 6683) and Black Sea (Ref. 188, 3397, 26334). Several subspecies have been recognized based on the number of gill rakers and geographical location (Ref. 10541); some have since been given species-status (Ref. 59043).
東北大西洋: 從斯堪的那維亞半島南部海岸到摩洛哥海岸, 包括不列顛群島與波羅的海.(參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 也整個的地中海 (參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442), 包括黑海.(參考文獻 26334) 一些亞種曾經公認的主要依據鰓耙數.(參考文獻 188) 在伯恩公約的附錄 3 中 (受保育的動物群).
Length at first maturity / 大小 / 重量 / 年齡
成熟度: Lm 32.5 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 60.0 cm SL 雄魚/尚未辨別雌雄; (Ref. 35388); common length : 40.0 cm SL 雄魚/尚未辨別雌雄; (Ref. 2945); 最大體重: 1.5 kg (Ref. 188); 最大年齡: 25 年 (Ref. 556)
背棘 (總數) : 0; 背的軟條 (總數) : 16 - 22; 臀棘: 0; 臀鰭軟條: 19 - 26; 脊椎骨: 49 - 59. Diagnosis: Body somewhat compressed, moderately deep with depth at pectoral fin less than head length, scutes apparent along belly (Ref. 188). Upper jaw notched, lower jaw fitting into it; no teeth on palatine and vomer; gillrakers fairly short and stout, total 30 to 80, shorter than gill filaments (Ref. 188, 59043). Usually a series of 4-8 black blotches behind gill opening, but sometimes a single blotch, the others faint or absent (Ref. 188, 40476, 59043). Alosa fallax resembles Alosa alosa, which has more and longer gillrakers and at most only 3 dark spots on flank (Ref. 188).
Body shape (shape guide): fusiform / normal; Cross section: compressed.
身體略微扁長形的, 中等深度但是深度在胸鰭少於頭長.(參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 上頜凹槽, 下頜嵌入它。 (參考文獻 188) 鰓耙非常短與矮胖的, 總計 30 到 80, 短於鰓絲.(參考文獻 188) 大又細的鱗片.(參考文獻 51442) 鱗甲明顯的沿著腹面.(參考文獻 188) 一個深色斑點後面被跟隨著 7 或者 8個相似的斑點的鰓裂沿著側面 ( 但是有時模糊的或不存在).(參考文獻 188) 也參考文獻 2196.
Amphihaline species (Ref. 51442), schooling and strongly migratory, but apparently not penetrating far up rivers (Ref. 188, 6683). Adults are usually found in open waters along the coast (Refs. 59043, 89486); juveniles are usually found along estuaries and near the shore (Ref. 59043), possibly making vertical diurnal movements synchronized with the tides; they remain in estuaries for over one year (Ref. 89630). Several landlocked (lake) non-migratory populations exist (Ref. 10541). Mostly anadromous, entering river mouths in March (Italy) or early June (northenr European rivers) to spawn in or above the tidal reaches; adults probably return to sea not long after spawning (Ref. 188, 6683). Eggs are demersal and widely scattered among sand or gravel on river bed (Ref. 118, 6683). Ichthyophagous, feeds on small fishes and crustaceans, the young taking the fry of herrings, sprats and gobies (Ref. 188, 51442). Females grow faster and are always larger than males of the same age (Ref. 10541). Very locally distributed due to pollution and impoundment of large rivers throughout Europe and most populations declined during the first decade of the 20th century, but seem to have stabilized at a low level since then (Ref. 59043). It has been suggested that members of the genus Alosa are hearing specialists with the American shad (Alosa sapidissima) having been found to detect and respond to sounds up to at least 180 kHz (Ref. 89631). This may aid in predator avoidance (e.g. cetaceans) (Ref. 89632). Hybridization between this species and the allis shad (Alosa alosa) has been reported from the Rhine (Ref. 89633) as well as rivers in France and Algeria (Ref. 10541). There is some evidence that indicates that shad hybrids may reproduce (Ref. 27567).
Amphihaline 種 (參考文獻 51442) ,群游性與強烈的迴游性, 但是顯然地不穿透在河川最上游.(參考文獻 188) 在五月或六月初中進入河川中有潮汐的河段在那裡或稍微向上產卵.(參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 產卵發生在晚上在沙地或礫石上面, 在一個 15-20 ° C. 的溫差 成魚在產卵之後返回大海, 而且稍後可以回到產卵第二個或第三個次.(參考文獻 51442) 卵是底棲的, 散佈在礫石或沙子.(參考文獻 188) 當他們發育的時候,魚苗沿河而下。 (參考文獻 188) 常吃魚的, 吃小魚與甲殼動物,幼魚捕食鯡魚,鯡魚與鰕虎魚的魚苗.(參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 蒙受河川污染與在某些程度上從河川人為障礙.(參考文獻 188) 在 3-4 年的一個年齡時性成熟而且在 30-40 公分的長度時性成熟。 (參考文獻 35388)
Life cycle and mating behavior
成熟度 | 繁殖 | 產卵場 | 卵 | 孕卵數 | 仔魚
Adults in the sea begin to congregate near mouths of estuaries in April. Enter estuaries and ascend rivers in May and June when water temperature is between 10-14 °C (Refs. 188, 51442, 59043, 89636). Males begin such movements at 2-3 years, females at 3-4 years (Ref. 59043). Although movement upstream is usually limited to a few kilometres above the brackish zone (Refs. 59043, 89486), spawning has also been reported in non-tidal freshwater areas up to 400 km upstream (Ref. 89637). Gametogenesis occurs in the estuaries. Early arrivals in the rivers are mostly males, with the sex ratio becoming more equal with the later arrivals (Ref. 42360). Spawning movements occur with spring tides and peak when river discharge levels are high (Refs. 89636, 89638). However, when flows are too high, movements upstream become limited (Refs. 89636, 89639). Spawn when water temperature is anywhere between 12-22 °C (Ref. 10541). Move to riverine spawning grounds at night; spawn in large, very noisy schools near surface and leave these areas before daybreak (Ref. 10541).
Spawning sites consist of sand and gravel areas with flowing water (Ref. 10541). Spent adults return to the sea and may spawn for 3-4 seasons throughout their lifetime (Refs. 30578, 51442, 59043). Most individuals will have lost 22 % of their body weight after spawning (Ref. 89640). There is some evidence that most individuals return to their natal rivers to spawn (Refs. 10541, 59043). Eggs either drift with the current or sink to the bottom (Ref. 59043, 89641). Eggs hatch after 2-8 days, depending on water temperature (optimal 15-25 °C) (Refs. 35387, 41851). Larvae and juveniles move towards the estuaries and river mouths during their first summer and to the sea at the end of their second year (Ref. 59043). Males mature mainly between the ages of 2-5 years, females between 3-7 years (Ref. 188, 2163, 10541). Length at maturity is between 30-40 cm total length (Ref. 88187).
東北大西洋: 從斯堪的那維亞半島南部海岸到摩洛哥海岸, 包括不列顛群島與波羅的海.(參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 也整個的地中海 (參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442), 包括黑海.(參考文獻 26334) 一些亞種曾經公認的主要依據鰓耙數.(參考文獻 188) 在伯恩公約的附錄 3 中 (受保育的動物群).
Whitehead, P.J.P., 1985. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid fishes of the world (suborder Clupeoidei). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the herrings, sardines, pilchards, sprats, shads, anchovies and wolf-herrings. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/1):1-303. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 188)
IUCN 瀕危狀態 (Ref. 130435: Version 2025-1)
無危 (LC) ; Date assessed: 26 June 2022
人類使用
漁業: 低經濟
工具
特別的報告
下載 XML
網路資源
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (參考文獻
123201): 8.7 - 19.3, mean 10.8 °C (based on 522 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (參考文獻
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00562 (0.00474 - 0.00667), b=3.06 (3.02 - 3.10), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
營養階層 (參考文獻
69278): 4.0 ±0.4 se; based on diet studies.
Generation time: 3.1 (2.2 - 4.8) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 14
growth studies.
回復力 (參考文獻
120179): 中等的, 族群倍增時間最少 1.4 - 4.4年 (K=0.21-0.38; tm=2-7; tmax=25; Fec>10,000).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate to high vulnerability (50 of 100).
🛈
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): Moderate vulnerability (44 of 100).
🛈
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 9.95 [4.94, 51.06] mg/100g; Iron = 0.495 [0.207, 1.198] mg/100g; Protein = 19.5 [17.1, 22.4] %; Omega3 = 1.53 [0.81, 2.92] g/100g; Selenium = 14.3 [7.1, 31.3] μg/100g; VitaminA = 14.2 [3.7, 52.6] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.288 [0.182, 0.505] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.