Oceanic, but sometimes found close inshore (Ref. 6871, 11230, 58302). Usually in surface waters (Ref. 30573), down to about 150 m (Ref. 26938, 11230). Coastal, epipelagic at 1->500 m (Ref. 58302). Isotope analysis has shown that shortfin mako is the highest level fish predator in oceanic waters off eastern Australia (Ref. 86961). Adults feed on bony fishes, other sharks (Ref. 5578), cephalopods; larger individuals may feed on larger prey such as billfish and small cetaceans (Ref. 6871, 58048). Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 43278, 50449). With 4-16 young of about 60-70 cm long (Ref. 35388, 26346). Gestation period lasts 15-18 months, spawning cycle is every 3 years. Some authors (Refs. 1661, 28081, 31395) have erroneously assumed that two age rings are deposited per year by this species, thus underestimating longevity, age at maturity, and resilience . These data have been removed and replaced by recent, verified estimates (Refs. 86586, 86587, 86588). Tagging in New Zealand indicates seasonal migrations (Ref. 26346). The presence of genetic differentiation in mitochondrial DNA across global populations (Ref. 36416) suggests dispersal may be male-biased, and that females may have natal site-fidelity. Shortfin mako has been shown to have a marked sexually segregated population structure (Ref. 86954). Shortfin mako is probably the fastest of all sharks and can leap out of the water when hooked (Ref. 6871). Potentially dangerous and responsible for unprovoked attacks on swimmers and boats (Ref. 13574). Utilized fresh, dried or salted, smoked and frozen; eaten broiled and baked (Ref. 9988). Valued for its fine quality meat as well as its fins and skin (Ref. 247). Oil is extracted for vitamins and fins for shark-fin soup (Ref. 13574). Jaws and teeth are also sold as ornaments and trophies (Ref. 9988). by Kabasakal & de Maddalena, 2011 reported a historical record of a larger specimen, caught in the Mediterranean Sea off Turkey, about 585 cm (TL estimated from photographs) (Ref. 106604). Maximum depth from Ref. 125614.
大洋性的, 但是有时发现近岸.(参考文献 6871,11230) 通常在水表面 (参考文献 30573), 向下至大约 150 公尺.(参考文献 26938,11230) 吃硬骨鱼类,其他的鲨鱼 (参考文献 5578) ,头足类动物; 较大的个体可能吃较大的猎物例如青旗鱼与小的鲸类。 (参考文献 6871) 卵胎生的, 胚胎吃产生于母亲的卵黄囊与其他的卵.(参考文献 50449) 多达 18 幼鱼在一胎.(参考文献 26346) 在纽西兰附以签条指出季节性的回游。 (参考文献 26346) 可能所有鯊魚的最快速的而且能從水中跳出來當鉤住.(參考文獻 6871) 可能危險而的原因未受刺激的攻擊游泳者與船.(參考文獻 13574) 生鮮使用, 乾燥或鹽醃, 煙燻與冷凍的; 吃火烤了而且燒烤了.(參考文獻 9988) 重要的是它的細品質肉了以及它的鰭與皮膚.(參考文獻 247) 油被吸取用於維他命與鰭用於魚翅湯。 (參考文獻 13574) 顎與齒也被賣作裝飾品與獎座。 (參考文獻 9988) 對 4-16個幼魚生產, 60-70 公分長.(參考文獻 35388)
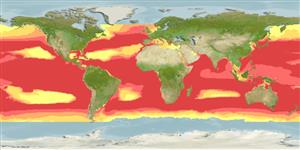
Preferred temperature (Ref.
115969): 9.7 - 24.4, mean 17.4 (based on 598 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.7813 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00646 (0.00386 - 0.01080), b=3.03 (2.88 - 3.18), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species & (Sub)family-body (Ref.
93245).
营养阶层 (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
回复力 (Ref.
120179): 低的, 最小族群倍增时间4.5 - 14 年 (rm=0.051; tm=8-20; tmax=32; Fec=4).
Prior r = 0.14, 95% CL = 0.09 - 0.21, Based on 3 full stock assessments.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (79 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): High vulnerability (62 of 100).