Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecología
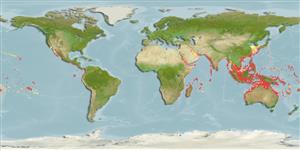
marino asociado a arrecife; rango de profundidad 0 - 80 m (Ref. 86942). Tropical; 35°N - 31°S, 30°E - 77°W
Indo-Pacific: from Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa, north to Mie Prefecture, Japan and east to southwestern coast of Baja California Sur, Mexico and Gulf of California to Ecuador (Ref. 9283).
Length at first maturity / Tamaño / Peso / Age
Maturity: Lm 32.5 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 120 cm TL macho / no sexado; (Ref. 11441); common length : 75.0 cm FL macho / no sexado; (Ref. 9283); peso máximo publicado: 15.0 kg (Ref. 30874)
Espinas dorsales (total): 8; Radios blandos dorsales (total): 18-20; Espinas anales 3; Radios blandos anales: 15 - 17.
Adults occur in deep lagoon and seaward reefs where they feed by rooting for crustaceans and fossorial invertebrates in the sand but they also feed on small fishes (Ref. 9710, 90102). Small juveniles live among the tentacles of jellyfish (Ref. 9710). Adults form schools and are also noted for their behavior to closely swim around sharks and other large fishes, and also follow divers (Ref. 10361). Juveniles particularly display this piloting behavior to gain protection from likely predators (Ref. 9710, 90102). Marketed fresh and salted or dried (Ref. 9283). Juveniles are used in the aquarium trade. Minimum depth reported taken from Ref. 128797.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Madurez | Reproducción | Puesta | Huevos | Fecundidad | Larva
Smith-Vaniz, W.F., 1995. Carangidae. Jureles, pámpanos, cojinúas, zapateros, cocineros, casabes, macarelas, chicharros, jorobados, medregales, pez pilota. p. 940-986. In W. Fischer, F. Krupp, W. Schneider, C. Sommer, K.E. Carpenter and V. Niem (eds.) Guia FAO para Identification de Especies para lo Fines de la Pesca. Pacifico Centro-Oriental. 3 Vols. FAO, Rome. (Ref. 9283)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
Human uses
Warning: mysqli::__construct(): (HY000/1040): Too many connections in /var/www/html/includes/func_getlabel.php on line 46
Can't connect to MySQL database (fbapp). Errorcode: Too many connections