| Squatinidae (Angel sharks) |
| 200 cm TL (male/unsexed) |
|
demersal; marine |
| Northwest Pacific: Japan, Yellow Sea, Korea, and northern China. |
|
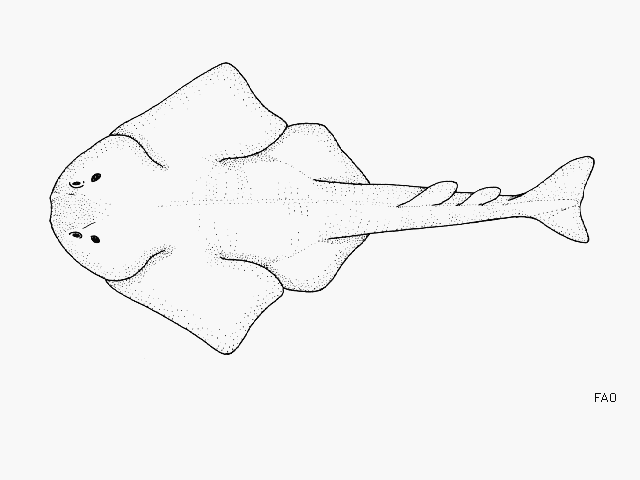
Dorsal spines (total): 0-0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 0-0; Anal spines: 0-0; Anal soft rays: 0-0. Japanese angelshark Squatina japonica has broad pectoral fins with rounded free rear tips, posterior margin nearly straight, inner margin strongly convex; nasal barbels simple and spatulate. Anterior nasal flaps smooth to weakly fringed; dermal folds on sides of head without lobes. Rear tip of inner margin of pelvic fins considerably anterior to origin of first dorsal; very short hypocercal tail. Rows of moderately large spines on midline of back and tail from head to dorsal fins and between fin bases, and on snout and above eyes. Body color blackish brown with small dark and pale spots; no ocelli (eye-like spot) (Ref. 247, 31369, 12951). |
| A little-known angelshark, found on or near the bottom (Ref. 247). Lives in sandy ground. A carnivore that eats benthic animals (Ref. 9137). Ovoviviparous (Ref. 50449). Utilized for human consumption and for preparation of shagreen (Ref. 247). |
|
Critically Endangered (CR); Date assessed: 29 August 2019 (A2d) Ref. (130435)
|
| traumatogenic |
Source and more info: www.fishbase.org. For personal, classroom, and other internal use only. Not for publication.