Common names from other countries
Élasmobranches (requins et raies) (sharks and rays) >
Torpediniformes (Electric rays) >
Torpedinidae (Electric rays)
Etymology: Torpedo: Latin, torpere = be sluggish (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Risso.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin; saumâtre récifal; profondeur 2 - 370 m (Ref. 4430). Subtropical; ? - 20°C (Ref. 10011); 60°N - 34°S, 19°W - 36°E (Ref. 114953)
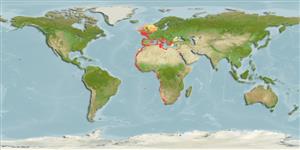
Eastern Atlantic: northern UK (less common in southern North Sea and Kattegat) to Cape of Good Hope, South Africa. Also in the Mediterranean Sea.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm 44.0, range 39 - 49 cm
Max length : 100.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 27000); common length : 60.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 114953); poids max. publié: 3.0 kg (Ref. 35388)
Description synthétique
Clés d'identification | Morphologie | Morphométrie
Épines dorsales (Total) : 0; Épines anales: 0; Vertèbres: 104 - 108. Disc-width around the same as its length, length and width 1,50 to 1,70 times in total length; dorsal fins more or less rounded, its base 1,50 times in its height (Ref. 39215).
Occurs in seagrass areas, rocky reefs, and adjacent soft bottoms (Ref. 12951). Avoids temperatures above 20°C (Ref. 10011). Nocturnal, usually burying itself during the day with only the eyes and spiracle jutting out (Ref. 12382). Feeds on small benthic fishes Trachurus, Mugil, Mullus, Dicentrarchus, Spondyliosoma, Boops, Labrus, Dascyllus, Pomacentrus) and crustaceans (Ref. 10011). Females outlive males; viviparous, neonates measuring 10-14 cm at birth (Ref. 10426). Produces 2-32 pups in a litter after a 10-month gestation (Ref. 12951, Ref. 114953). Males reaches maturity at ca. 30 cm TL, females at ca. 40 cm TL; born at 10-14 cm TL (Ref. 114953). Electrocytes start developing when the embryo weighs about 1 g; electric organs functional before birth and newborns can use their electric organ discharge (EOD) in capturing prey (Ref. 10428). Can produce electric discharges of up to 200 volts; EOD frequency up to 600 Hz. Jumps on fast-moving prey, paralyzing it with its EOD (Ref. 27000).
Exhibit ovoviparity (aplacental viviparity), with embryos feeding initially on yolk, then receiving additional nourishment from the mother by indirect absorption of uterine fluid enriched with mucus, fat or protein through specialised structures (Ref. 50449).
Stehmann, M. and D.L. Bürkel, 1984. Torpedinidae. p. 159-162. In P.J.P. Whitehead, M.-L. Bauchot, J.-C. Hureau, J. Nielsen and E. Tortonese (eds.) Fishes of the north-eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean. UNESCO, Paris. Vol. 1. (Ref. 2803)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
CITES (Ref. 128078)
Not Evaluated
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: sans intérêt; Aquarium: Aquariums publics
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
115969): 10.1 - 19.2, mean 14.1 (based on 392 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5005 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01820 (0.01478 - 0.02241), b=2.93 (2.87 - 2.99), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Faible, temps minimum de doublement de population : 4,5 à 14 années (Fec=5-32).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): High vulnerability (60 of 100).