Common names from other countries
>
Salmoniformes (Salmons) >
Salmonidae (Salmonids) > Salmoninae
Etymology: Salvelinus: Old name for char; it is the same root of german "saibling" = little salmon (Ref. 45335); fontinalis: fontinalis meaning living in springs (Ref. 1998).
More on author: Mitchill.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecología
marino; agua dulce; salobre bentopelágico; anadromo (Ref. 120291); rango de profundidad 15 - 27 m (Ref. 3899). Temperate; 0°C - 25°C (Ref. 35682); 61°N - 34°N, 124°W - 52°W (Ref. 86798)
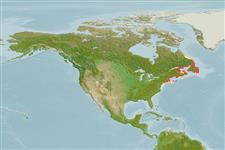
North America: native to most of eastern Canada from Newfoundland and Labrador to western side of Hudson Bay; south in Atlantic, Great Lakes, and Mississippi River basins to Minnesota and northern Georgia (Applachian Mountains), USA; headwaters of Chattahoochee River (Gulf basin). Introduced widely in North America and temperate regions of other continents. Several countries report adverse ecological impact after introduction.
Tamaño / Peso / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 86.0 cm SL macho / no sexado; (Ref. 7248); common length : 26.4 cm TL macho / no sexado; (Ref. 12193); peso máximo publicado: 8.0 kg (Ref. 100229); edad máxima reportada: 24 años (Ref. 72501)
Espinas dorsales (total) : 3 - 4; Radios blandos dorsales (total) : 8 - 14; Espinas anales: 3 - 4; Radios blandos anales: 8 - 14; Vértebra: 58 - 62. Distinguished by the combination of dark green marbling on its back and dorsal fin and by the red spots with blue halos on its sides (Ref. 27547). Pelvic fins with axillary process; caudal nearly straight or with a shallow indentation (Ref. 27547). Color varies, but generally rather green to brownish on back, marked with paler vermiculations or marbling that extend onto the dorsal fin and sometimes the caudal; sides lighter than back, marked with numerous pale spots and some red spots, each of the latter surrounded by a blue halo; anal, pelvic and pectoral fins with a white leading edge followed by a dark stripe, the rest of the fins reddish (Ref. 27547). In spawning fish the lower sides and fins become red (Ref. 27547). Sea-run fish are dark green above with silvery sides, white bellies and very pale pink spots (Ref. 27547). Caudal fin with 19 rays (Ref. 2196).
Occurs in clear, cool, well-oxygenated creeks, small to medium rivers, and lakes (Ref. 5723, 86798). Nerito-pelagic (Ref. 58426). Anadromous in some populations (Ref. 86798). In its native range, general upstream movements have been observed in early spring, summer and late fall; downstream movements, in late spring and fall (Ref. 28546, 28548, 28549, 28550). Some fish, popularly known as salters, run to the sea in the spring as stream temperature rises, but never venture more than a few kilometers from river mouths. It may remain at sea for up to three months (Ref. 28546, 28549, 28551). Feeds on a wide range of organisms including worms, leeches, crustaceans, insects (chironomids, caddisflies, blackflies, mayflies, stoneflies and dragonflies (Ref. 5951), mollusks, fishes and amphibians (Ref. 3348, 10294); also small mammals (Ref. 1998). Stomachs of some individuals contained traces of plant remains (Ref. 1998). There are reports of introduced fish reaching 15 years of age in California, USA (Ref. 28545). Cultured for food and for stocking (Ref. 27547). Extensively used as an experimental animal (Ref. 1998). Marketed fresh and smoked; eaten fried, broiled, boiled, microwaved, and baked (Ref. 9988).
Courtship begins with a male attempting to drive a female toward suitable spawning gravel. A receptive female chooses a spot and digs a redd. While the female is digging, the male continues courtship activity, darting alongside the female and quivering, swimming over and under her and rubbing her with his fins; most of the time however, is spent driving off other males. When the redd is completed, the pair enter the nest and deposit eggs and milt. After spawning the female covers the eggs by sweeping small pebbles at the downstream edge of the redd upstream. Once the eggs are completely covered, she moves to the upstream end of the redd and begins digging a new redd (Ref. 27547).
Page, L.M. and B.M. Burr, 2011. A field guide to freshwater fishes of North America north of Mexico. Boston : Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 663p. (Ref. 86798)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES (Ref. 128078)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Potential pest
Human uses
Pesquerías: escaso valor comercial; Acuicultura: comercial; pesca deportiva: si; Acuario: Acuarios públicos
Herramientas
Special reports
Download XML
Fuentes de Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
115969): 1.5 - 10.7, mean 4.5 (based on 47 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00912 (0.00779 - 0.01068), b=3.03 (2.98 - 3.08), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Nivel trófico (Ref.
69278): 3.3 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
Resiliencia (Ref.
120179): Medio, población duplicada en un tiempo mínimo de 1.4-4.4 años (tm=1-3; tmax=7).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): High vulnerability (63 of 100).